Table of Contents
How Artificial Intelligence is Preventing Blindness
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing many aspects of healthcare, and eye care is no exception. Blindness and vision impairment affect millions worldwide, often caused by chronic diseases such as diabetic retinopathy, glaucoma, and age-related macular degeneration (AMD). These conditions progress silently in many cases, making early detection and intervention crucial for preventing permanent vision loss. AI technology is now helping doctors identify these eye diseases earlier, faster, and more accurately than ever before.
The Challenge of Early Detection in Eye Diseases
One of the biggest challenges in preventing blindness is that many eye diseases develop gradually and without obvious symptoms until significant damage has occurred. Traditional screening methods, such as manual examination of retinal images by specialists, can be time-consuming, subjective, and limited by the availability of trained professionals—especially in underserved or rural areas.
How AI Changes the Game
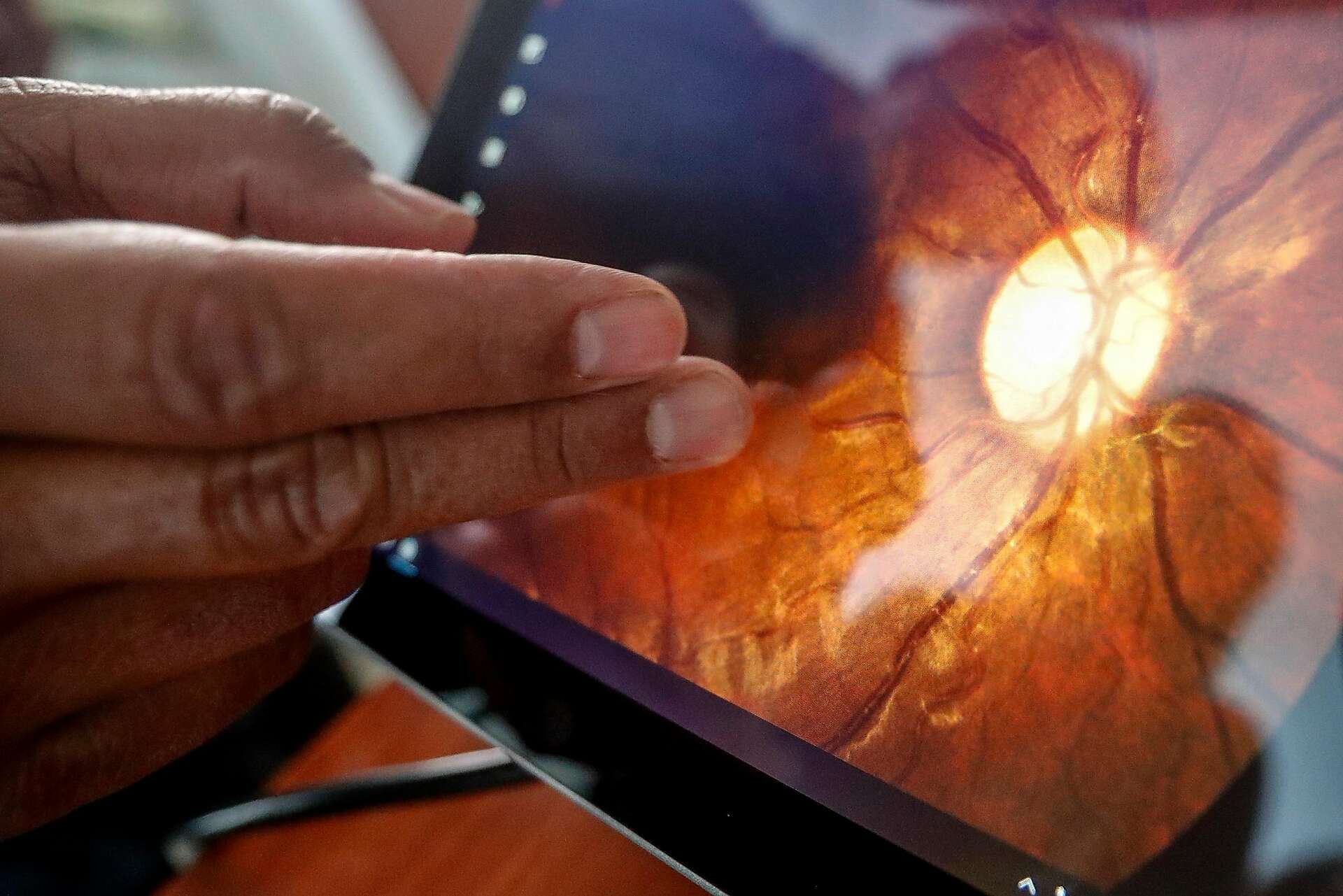
AI systems, particularly those powered by deep learning and neural networks, have the ability to analyze vast amounts of imaging data quickly and identify subtle patterns that might escape even expert human eyes. These algorithms are trained on thousands or millions of retinal scans, learning to recognize early signs of diseases such as:
Diabetic Retinopathy: A diabetes-related condition that damages blood vessels in the retina.
Glaucoma: Often called the “silent thief of sight,” glaucoma damages the optic nerve gradually.
Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD): A leading cause of vision loss in older adults, affecting central vision.
By automating image analysis, AI tools can flag high-risk patients for further examination or treatment, reducing delays in care.
Real-World Applications
Automated Retinal Screening: Several AI-powered platforms have been approved by regulatory agencies to assist or independently conduct diabetic retinopathy screening. For example, some clinics use AI software that analyzes fundus photographs within minutes, providing instant feedback to healthcare providers.
Telemedicine and Remote Access: AI integration with portable retinal cameras and smartphones is bringing eye screening to remote and underserved communities worldwide. This democratization of screening can catch diseases earlier, even where eye specialists are scarce.
Continuous Monitoring: AI algorithms are also being developed to monitor disease progression over time, helping doctors personalize treatment plans and adjust therapies based on real-time data.
Benefits Beyond Detection
AI doesn’t just improve diagnosis speed—it also helps reduce healthcare costs by optimizing resource use, minimizes human error, and enables large-scale population health management. Furthermore, by facilitating earlier treatment, AI contributes to preserving patients’ quality of life and reducing the emotional and economic burden of vision loss.
Challenges and Future Directions
While AI holds tremendous promise, challenges remain. Algorithms require large, diverse datasets for training to ensure accuracy across different populations. Integration into clinical workflows must prioritize patient privacy and data security. Ongoing collaboration between clinicians, data scientists, and regulatory bodies is essential to refine and expand AI’s capabilities.
Looking ahead, combining AI with other emerging technologies such as genetic testing and wearable sensors could further enhance personalized eye care and blindness prevention.
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence is reshaping eye care by enabling earlier, more precise detection of sight-threatening diseases, especially in populations that lack easy access to specialist care. By harnessing the power of AI, we can reduce preventable blindness worldwide and ensure healthier vision for millions. Staying informed about these advances empowers patients and providers alike to embrace innovative tools that protect one of our most valuable senses—our sight.
Dr. Alejandro Espaillat is a board-certified ophthalmologist and fellow of the American College of Surgeons, specializing in cataract surgery, diabetic eye disease, and the application of artificial intelligence in vision care.